

A common dental condition known as dental erosion is caused by acid attack, and it occurs when the tooth loses its enamel. Acid attacks the enamel and destroys it thereby exposing the sensitive part of your tooth. The enamel is a strong protecting coat covering the tooth. It protects the sensitive dentine beneath the tooth.
This dentine is exposed when the enamel is worn away, and this, in turn, leads to sensitivity and pain.
Erosion appears as hollows in the teeth — it shows the general wearing away of the surface of the tooth and the biting edges. This will expose the dentine under the teeth. The dentine has a darker and yellower colour than the enamel.
Your teeth can also be more sensitive to cold, heat, and acidic foods and drinks because the dentine is sensitive.
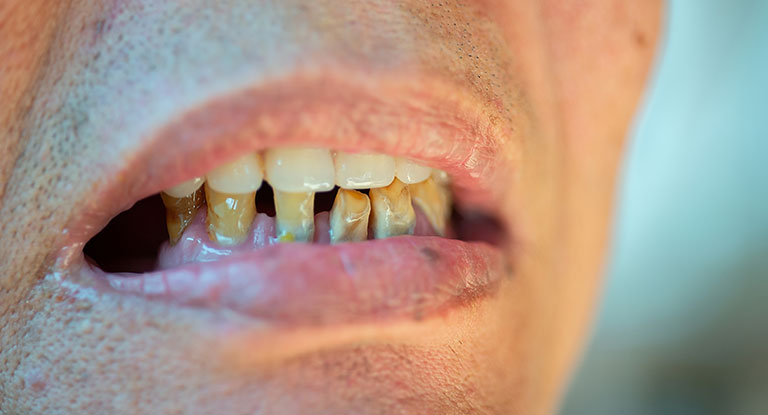
Dental erosion is a condition commonly caused by acidic foods and drinks. Whenever you take these in, it makes your enamel soft for a while, and this leads to the loss of some of its mineral content.
After a while, your saliva will slowly reduce the acidity in your mouth and bring it back to the natural balance. This gives your enamel time to recover and get hard again. However, your enamel won’t have the chance to heal itself and recover. If this attack is too often, tiny bits of enamel will be brushed away, and you will begin to lose the surface of your teeth.
Yes, some medical conditions can trigger dental erosion, and one of this is bulimia nervosa, a mental condition in which people try to lose weight by making themselves sick. They do these by inducing a vomit after every meal. This affects your enamel because they are high levels of stomach acids in the vomit and they erode your enamel when they come in contact with your tooth.
In another medical condition called Gastroesophageal reflux, acids produced by the stomach can come up into the mouth. This also can damage the enamel of your tooth when it comes in contact with it.
People who suffer from oesophageal problems, hiatus hernia, and excessive intake of alcohol can also suffer from dental erosion because these conditions induce vomiting.
Yes, you can prevent dental erosion by avoiding certain types of foods, most especially acidic foods and drinks because they cause erosion of the enamel. Any food or drink with a pH higher than 5.5 should not be taken; it is highly acidic and can harm your teeth. Examples of these are sodas, carbonated drinks, pops, and fizzy drinks.
Also, remember that products labelled “diets” are harmful and are also acidic. They also contain extremely high levels of sugars which can also damage your teeth. Even flavoured fizzy water can damage your enamel if taken in excess, even though they contain weak acids, they can still harm your teeth.
Fruits and fruits juices are also examples of acidic foods and drinks, most especially citrus fruits such as oranges and lemons. They contain natural acids that are harmful to your teeth, and they can erode your enamel if you take them often.
Designer drinks, coolers, and alcopops, which are fizzy and contain acidic fruits can also damage your enamel and cause erosion. The best drink for the teeth is plain water, milk is also good because it neutralises acids in the mouth.
Sports drinks are not that safe because most of them contain ingredients that can cause both dental erosion and tooth decay. Athletes can drink plain water or coconut milk to fight dehydration.
Dehydration is not good for the body — it causes dry mouth, bad breath, and other health problems.
There are several things you can do to prevent dental erosion, and some of them are:
Aside from fluoride toothpaste, your dentist will suggest mouthwash containing fluoride, and he/she can also apply fluoride varnish on your teeth every six months.
They can also prescribe a toothpaste with higher fluoride content for you.
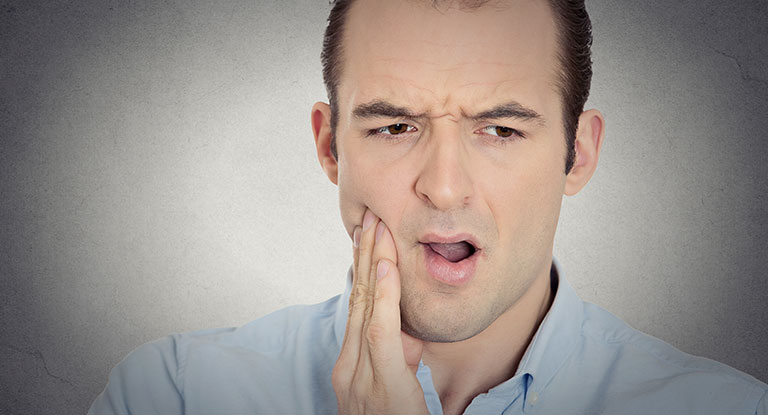

Dental erosion is not treated in all cases, but regular check-up and advice are given by the dentist to prevent the problem from getting worse and progressing into more severe conditions.
If the dentist checks your tooth and sees the need for treatment, the enamel and the dentine underneath is protected to prevent sensitivity. The affected tooth can be repaired by bonding a filing on it; however, a veneer can be fitted on the tooth if it is severe.
The cost of treatment varies, and this depends on the type of treatment that is best suited for your case.
Our dental team will discuss all the treatment options with you and advice you on the best treatment for your case. Contact our team of dentists today and we will advise you on how best to prevent and manage this condition.